Bi-Vacuum, Sub-elementary particles and Dynamic Model of Corpuscle - Wave Duality
p. 121-142
Abstract
Our Dynamic Model of Corpuscle-Wave [C ⇌ W] Duality elaborated, is based on the new notion of bi-vacuum. The hypothesis of bi-vacuum postulates the existence of positive (real) and negative (mirror) vacuum as two non mixing 'oceans' of superfluid quantum liquid from virtual quanta of the opposite energies. The unified system of positive and negative vacuum is termed: bi-vacuum. It is assumed to be an infinitive source of bi-vacuum fermions with half-integer positive (BVF↑) and negative (BVF↓) spins and bi-vacuum bosons (BVB0) of zero spin. In accordance to our model, (BVF↑) and (BVF↓) represent correlated pairs of in-phase [real rotor+ mirror rotor] and [real antirotor + mirror antirotor] of opposite polarization, correspondingly. For the other hand, (BVB0), formed by the counter phase [real rotor+ mirror antirotor] may be considered as intermediate stage of conversion between (BVF↑) and (BVF↓). The rotors and antirotors of all of these three kind of bi-vacuum excitations, as symmetrically excited levels of energy in realms of positive (real) and negative (mirror) vacuum, are separated from each other by energetic gap, which may be different.
The external resulting impulse (momentum) of all of three kind of symmetric bi-vacuum excitations: PBVB0, PBVF↑ and PBVF↓ is equal to zero as far their external group velocity is zero. This means that external virtual wave B length of these primordial excitations, as a ratio of Plank constant to impulse of virtual rotor (λext = h/PBVB0,BVF↑ → ∞) is tending to infinity. Such condition means infinive virtual Bose condensation of bi-vacuum and its nonlocal properties. The symmetric bi-vacuum excitations: BVB0, BVF↑ and BVF↓ may have a broad spectra of radiuses and related energetic gaps, determined by energy and effective mass of excitations. In primordial vacuum in the absence of matter the number of BVF↑ and BVF↓ should be equal, following the Pauli principle.
The sub-elementary particles and sub-elementary antiparticles in corpuscular [C] phase represent the asymmetrically excited bi-vacuum fermions:
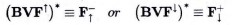
in form of 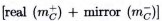 of mass-dipole with opposite spins (S = ±½) and charge (e±). The spatial image of this mass-dipole is a correlated dynamic pair : [real vortex + mirror rotor]. The real inertial (
of mass-dipole with opposite spins (S = ±½) and charge (e±). The spatial image of this mass-dipole is a correlated dynamic pair : [real vortex + mirror rotor]. The real inertial (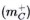 ) and inertialess (
) and inertialess (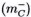 ) mass are the result of bi-vacuum symmetry shift, accompanied by sub-elementary particle or sub-elementary antiparticle origination, depending on the sign of shift. The corpuscular [C] and wave [W] phases of sub-elementary particles/antiparticles are considered in our model as two alternative phase of de Broglie wave (wave B), which are in dynamic equilibrium [C ⇌ W]. The frequency of [C ⇌ W] pulsation is equal to frequency of quantum beats between real and mirror corpuscular states. It the full article (Kaivarainen, 2000) I demonstrate, that basically new approach, developed in this work, elucidate the quantum roots of Golden mean and may serve as effective way to unification of electromagnetic, gravitational and temporal fields.
) mass are the result of bi-vacuum symmetry shift, accompanied by sub-elementary particle or sub-elementary antiparticle origination, depending on the sign of shift. The corpuscular [C] and wave [W] phases of sub-elementary particles/antiparticles are considered in our model as two alternative phase of de Broglie wave (wave B), which are in dynamic equilibrium [C ⇌ W]. The frequency of [C ⇌ W] pulsation is equal to frequency of quantum beats between real and mirror corpuscular states. It the full article (Kaivarainen, 2000) I demonstrate, that basically new approach, developed in this work, elucidate the quantum roots of Golden mean and may serve as effective way to unification of electromagnetic, gravitational and temporal fields.
Index
Text
References
Bibliographical reference
Alex Kaivarainen, « Bi-Vacuum, Sub-elementary particles and Dynamic Model of Corpuscle - Wave Duality », CASYS, 10 | 2001, 121-142.
Electronic reference
Alex Kaivarainen, « Bi-Vacuum, Sub-elementary particles and Dynamic Model of Corpuscle - Wave Duality », CASYS [Online], 10 | 2001, Online since 10 July 2024, connection on 25 February 2026. URL : http://popups.lib.uliege.be/1373-5411/index.php?id=1247
Author
Alex Kaivarainen
University of Turku, JBL, FIN-20520, Turku, Finland